Don't Stuck in the Waiting Room!
Register Online Before You Arrive.
We have up-to-date schedules, contact information, and allow you to make appointments online.
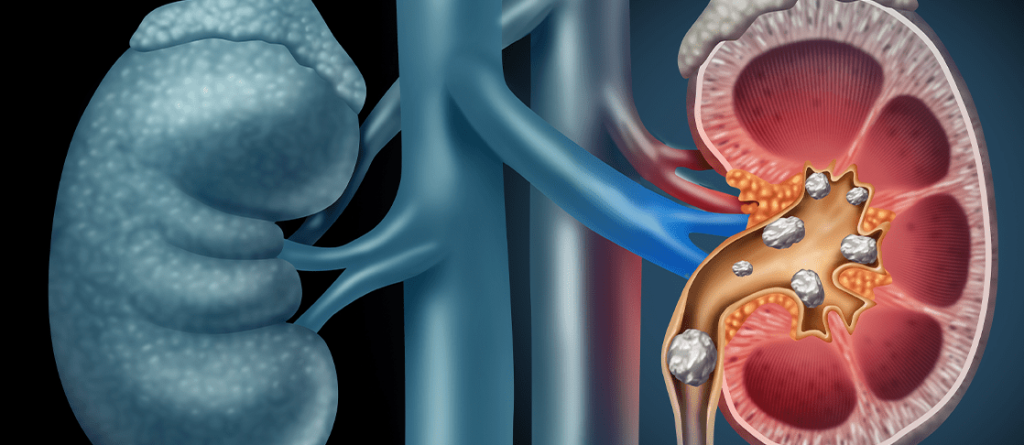
Definition of Kidney and Urinary Tract Stones
Kidney and urinary tract stones form when minerals crystallize in the urinary tract and come together to create hard structures. These stones can form at any point from the kidneys to the bladder. Stones usually begin in the kidneys but can travel through the urinary tract, causing pain and other symptoms. The size of stones can vary; some are as small as a grain of sand, while others can be several centimeters in diameter.
Prevalence and Importance of the Disease
Kidney and urinary tract stones are a common health problem worldwide. This condition, particularly prevalent in the adult population, can significantly reduce quality of life. Early diagnosis and proper management of stone disease are critical to preventing complications. Therefore, raising awareness about stone disease is necessary from a public health perspective.
Types of Stones
Calcium Stones: The Most Common Type
Causes and Risk Factors
Calcium stones are the most common type of kidney stones and usually consist of calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate. High levels of calcium or oxalate, low fluid intake, and certain dietary habits can contribute to the formation of these stones. Additionally, genetic predisposition and certain metabolic disorders are among the risk factors.
Symptoms and Complications
Calcium stones can cause severe kidney pain, blood in the urine, and frequent urination. Stones can lead to blockages in the kidneys or urinary tract, causing infections and kidney damage. Therefore, early detection and treatment of symptoms are important.
Struvite Stones: Infection-Related
Impact of Infections on Stone Formation
Struvite stones form as a result of urinary tract infections. Substances produced by bacteria during infection cause struvite stones to grow and spread. These stones usually grow quickly and can adversely affect kidney function.
Symptoms and Treatment Options
Struvite stones can cause symptoms similar to urinary tract infections: fever, chills, burning sensation during urination, and foul-smelling urine. Treatment may include controlling the infection and surgically removing the stones.
Uric Acid Stones: Metabolic Problems
Connection to Gout and Dehydration
Uric acid stones form due to high uric acid levels. People with gout and those who do not drink enough fluids are at higher risk for these stones. Dietary and lifestyle changes are important to prevent uric acid stones.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing uric acid stones involves low-purine diets, drinking plenty of water, and alkalinizing the urine. Treatment options include medications and surgical interventions.
Cystine Stones: Genetic Factors
Rare but Significant
Cystine stones form due to a genetic disorder called cystinuria. This condition arises because the kidneys cannot adequately dissolve the amino acid cystine. Although cystine stones are rare, they can be challenging to treat and have a high recurrence risk.
Diagnosis and Management
Urine tests and imaging techniques diagnose cystine stones. Treatment involves surgically removing the stones and using diet and medications to prevent recurrence.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Predisposition: Family History
Genetic factors play a significant role in the formation of kidney and urinary tract stones. Individuals with a family history of stone disease are at higher risk for stone formation.
Dietary Factors: High Salt and Protein Intake
Diets high in salt and protein can increase the risk of kidney stone formation. Salt can raise calcium levels in the urine, triggering stone formation, while protein can increase uric acid levels.
Dehydration: Importance of Fluid Intake
Adequate fluid intake is crucial in preventing kidney stones. Dehydration can cause minerals in the urine to concentrate, leading to stone formation.
Medical Conditions: Hyperparathyroidism, Obesity, etc.
Certain medical conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, obesity, and diabetes can increase the risk of kidney stones. These conditions can cause metabolic imbalances and changes in urine chemistry.
Medications: Impact on Stone Formation
Some medications can trigger the formation of kidney stones. For instance, excessive amounts of vitamin D or calcium supplements can increase the risk of forming calcium stones.
Environmental Factors: Climate and Geography
Individuals living in hot climates have a higher risk of dehydration, which can increase kidney stone formation. Additionally, the mineral content of water sources in certain geographical regions can influence stone formation.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms: Pain, Blood in Urine, Frequent Urination
Kidney stones typically present with severe flank pain, visible blood in the urine, and frequent urination. These symptoms can vary depending on the size and location of the stone.
Severe Symptoms: Fever, Nausea, Vomiting
In more severe cases, kidney stones can cause symptoms such as fever, nausea, and vomiting. These conditions can signal complications such as infection or kidney blockage.
Diagnostic Tests: Imaging and Urine Analysis
Ultrasound: Non-invasive and Effective
Ultrasound is a commonly used non-invasive imaging method for diagnosing kidney stones. It provides information about the size and location of the stones.
CT Scan: Detailed Imaging
A CT scan offers detailed imaging of kidney stones and is particularly effective in detecting small stones.
X-ray: When It Is Useful
X-rays can be helpful in detecting certain types of kidney stones. However, not all stone types are visible on X-rays.
Urine Tests: Determining the Type of Stone
Urine tests play an important role in determining the type of stone. These tests measure the levels of minerals and other substances in the urine.
Treatment Options
Conservative Management: Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
The first step in treating kidney stones is lifestyle and dietary changes. Drinking plenty of water and reducing salt and protein intake can help prevent stone formation.
Medications: Pain Relief and Stone Passage
Alpha Blockers: Facilitating Stone Passage
Alpha blockers help widen the urinary tract, making it easier for stones to pass.
Pain Relievers: Managing Pain Episodes
Pain relievers are used to alleviate the severe pain caused by kidney stones.
Surgical Interventions: When Surgery Is Necessary
Large or treatment-resistant stones may require surgical intervention.
Ureteroscopy: Minimally Invasive Technique
Ureteroscopy is a minimally invasive technique that uses a thin tube inserted into the urinary tract to remove stones.
Shock Wave Lithotripsy (SWL): Stone Fragmentation
SWL uses external shock waves to break stones into small pieces.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): For Larger Stones
PCNL is a surgical technique used to remove large kidney stones. This method requires accessing the kidney through a small incision in the skin.
Post-Treatment Care: Preventing Recurrence
Post-treatment care is important to prevent the recurrence of kidney stones. Regular doctor visits and lifestyle changes are critical in this process.
Preventive Measures
Dietary Adjustments: Foods to Include and Avoid
High Fluid Intake: Staying Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water keeps urine diluted and prevents stone formation.
Low Sodium Diet: Reducing Risk
Reducing sodium intake prevents calcium buildup in the urine and lowers the risk of stone formation.
Calcium Intake: Balancing Levels
Balancing calcium intake is especially important in preventing calcium stones.
Regular Check-ups: Importance of Monitoring
Regular doctor check-ups play a critical role in the early diagnosis and treatment of kidney stones.
Medications: Preventing New Stones
Potassium Citrate: Alkalizing Urine
Potassium citrate can prevent stone formation by increasing urine pH levels.
Lifestyle Changes
Healthy Eating Habits
Healthy eating habits play a significant role in preventing kidney stones. A balanced diet can reduce stone formation.
Adequate Water Consumption
Drinking enough water daily ensures the kidneys function properly and helps prevent stone formation.
Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise improves overall health and reduces the risk of kidney stones.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Herbal Remedies and Natural Methods
Herbal remedies and natural methods can support the prevention and treatment of kidney stones. However, these methods must be applied under medical supervision.
Acupuncture and Other Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture and other alternative therapies can be used for pain management and to support overall health.
Stone Disease in Children and Pregnant Women
Symptoms and Treatment of Stone Disease in Children
Kidney stones in children can occur due to genetic factors and dietary habits. Symptoms include abdominal pain, blood in urine, and frequent urination. Treatment varies depending on the size and location of the stone.
Management and Precautions for Stone Disease in Pregnant Women
Kidney stones can be more common in pregnant women due to hormonal changes and increased pressure in the urinary tract. In this case, it is important to choose safe and effective treatment methods.
Psychological Effects and Support
Psychological Effects of the Disease
In addition to physical discomfort, kidney stones can also have psychological effects. Constant pain and recurring stones can lead to issues such as stress and anxiety.
Psychological Support and Counseling Services
Psychological support and counseling services play an important role in maintaining the emotional and psychological health of patients with kidney stones.
Advanced Technology and Research
New Treatment Methods and Technological Developments
New technologies and treatment methods in the medical field allow kidney stones to be managed more effectively and safely. Innovations such as laser treatment and robotic surgery can speed up the recovery process for patients.
Future Research Directions and Expectations
Research on kidney stones helps us better understand the causes of the disease and develop more effective treatment methods. Future research aims to increase the knowledge base in this area.
Conclusion
Management and Prevention of Stone Disease
The management and prevention of kidney and urinary tract stones require a holistic approach. Proper nutrition, adequate water consumption, and regular medical check-ups can help prevent stone formation.
Tips for Overcoming the Disease
To cope with kidney stone disease, it is important to follow lifestyle changes and doctor recommendations. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and not neglecting regular check-ups will be effective in preventing the recurrence of the disease.
DO YOU NEED HELP?
Request a Callback Today!
We will usually contact you within 24 hours of your request.
