Don't Stuck in the Waiting Room!
Register Online Before You Arrive.
We have up-to-date schedules, contact information, and allow you to make appointments online.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Introduction: What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
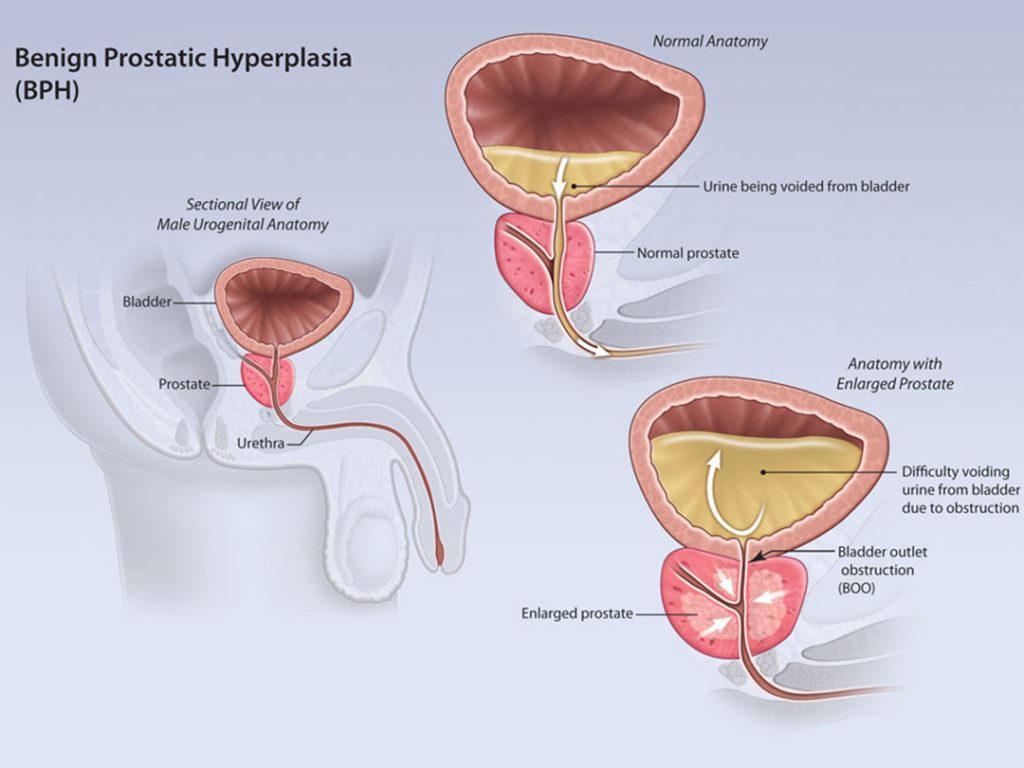
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common health condition characterized by the enlargement of the prostate gland as men age. The prostate is part of the male reproductive system and is located around the urethra. This growth is typically non-cancerous but can compress the urinary tract, causing discomfort and various symptoms. BPH is considered a natural part of aging for men but can become a serious issue affecting quality of life.
Definition and Basics of BPH
BPH is defined as the benign (non-cancerous) enlargement of the prostate gland. The prostate gland plays a role in the production of urine and semen in the male reproductive system. BPH results in the narrowing of the urethra due to the enlargement of the prostate gland, making urination difficult. This condition is usually seen in men over 50, and its frequency increases with age.
Function and Importance of the Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is a crucial part of the male reproductive system and produces fluid that forms semen. Additionally, the prostate gland, located around the urethra, functions like a valve controlling the passage of urine through the urethra. A healthy prostate gland performs these functions efficiently, but BPH can impair these functions, causing pressure on the urinary tract.
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia involves the enlargement of the prostate gland, leading to compression of the urinary tract. This condition occurs due to the generally harmless growth of tissues surrounding the prostate. Unlike prostate cancer, BPH is non-cancerous and typically progresses slowly. However, it can create difficulties and discomfort during urination.
General Characteristics of BPH
The main characteristics of BPH include difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and nocturia (waking up at night to urinate). The enlargement of the prostate gland narrows the urinary tract, obstructing urine flow and making it hard to fully empty the bladder. Furthermore, the growth of the prostate gland can cause pressure on the urinary tract, leading to discomfort and pain.
Differences Between Prostate Enlargement and Cancer
The differences between prostate enlargement and prostate cancer are significant. BPH is a benign (non-cancerous) enlargement, is non-cancerous, and is treatable. Prostate cancer, on the other hand, is a malignant condition that can spread rapidly and lead to more serious health problems. Prostate cancer typically presents different symptoms and has a more complex diagnosis.
Symptoms and Signs of BPH
The symptoms of BPH are usually related to urination. Symptoms can vary from person to person but typically include:
Increased Urination Frequency and Nighttime Urination
One of the most common symptoms of BPH is the frequent need to urinate. Increased frequency of nighttime urination can lead to insomnia and decreased quality of life. This condition is a result of pressure on the urinary tract, leading to increased nighttime urine production.
Weak and Difficult Urine Flow
The enlargement of the prostate gland can weaken urine flow and cause difficulties during urination. The urine flow is often intermittent, and completely emptying the bladder becomes challenging. This condition can lead to residual urine in the bladder and, consequently, urinary tract infections.
Urinary Incontinence and Leakage
BPH can lead to urinary incontinence and leakage. The enlargement of the prostate gland can weaken bladder muscles and make it harder to control urine. This situation can lead to social and psychological problems and significantly affect a person’s quality of life.
Other Symptoms Associated with Prostate Enlargement
Apart from urinary symptoms, BPH can cause other discomforts. Specifically, prostate enlargement can lead to tension and discomfort in the bladder wall. Additionally, due to the impact on nerves surrounding the prostate gland, there may be sensations of pain and discomfort.
Causes and Risk Factors of BPH
The exact causes of BPH are not fully understood, but several factors are believed to be influential.
Impact of Age and Genetic Factors
Age is one of the most significant risk factors for BPH. The likelihood of prostate gland enlargement increases as men age. Genetic factors may also play a role; individuals with a family history of BPH may be more frequently affected by this condition.
Hormonal Changes and BPH
Hormonal changes play an important role in the development of BPH. Specifically, changes in testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels can lead to prostate gland enlargement. These hormones can promote the growth of the prostate gland.
Role of Lifestyle and Dietary Habits
Lifestyle and dietary habits can also affect BPH. Diets high in fat, excessive alcohol consumption, and insufficient exercise can increase the risk of BPH. A healthy diet and regular exercise play an important role in maintaining prostate health.
Diagnosis Methods for BPH
The diagnosis of BPH is usually made through several tests and examinations.
Physical Examination and Doctor’s Checkups
During a physical examination, doctors may perform a rectal exam to evaluate the prostate gland. This examination is used to assess the size and firmness of the prostate gland. Additionally, the patient’s medical history and symptoms are taken into consideration.
Blood Tests and Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
Blood tests and the PSA test can help evaluate prostate health. The PSA test measures the level of a protein secreted by the prostate gland and can provide information about the presence of BPH. However, high PSA levels do not always indicate BPH and need to be confirmed with other tests.
Ultrasound and Other Imaging Methods
Ultrasound is used to assess the size and shape of the prostate gland. This imaging method is effective for measuring the size of the prostate and determining if there are any blockages in the urinary tract. Other imaging methods may include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Urine Flow Tests and Other Diagnostic Tools
Urine flow tests measure how quickly and efficiently urine is expelled. These tests are used to assess the obstruction created by the prostate gland in the urinary tract. Additionally, other tests such as bladder ultrasound can be used to measure residual urine.
Treatment Options for BPH
BPH treatment generally varies depending on the symptoms and severity of the enlargement.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Management
Lifestyle changes can be effective in alleviating BPH symptoms. Habits such as consuming plenty of fluids, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and engaging in regular exercise can improve the urination process. Additionally, regularly visiting the bathroom to relax the urinary tract can be helpful.
Medication Treatment and Effective Drugs
Medication treatment is frequently used to control BPH symptoms. Drugs such as alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can reduce prostate gland enlargement and improve urine flow. Medication treatment is usually used in conjunction with regular doctor checkups.
Minimally Invasive Methods and Surgical Intervention
Minimally invasive methods are techniques used to reduce prostate gland enlargement. These methods include laser treatment, microwave therapy, and endoscopic procedures. Surgical intervention may be necessary in more severe cases and when other treatment methods are ineffective. These operations involve removing part or all of the prostate gland.
Alternative and Natural Treatment Methods for Prostate Enlargement
Alternative and natural treatment methods may be beneficial for some patients. Specifically, herbal supplements, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants can help support prostate health. However, more research is needed on the effectiveness and reliability of these methods.
Living with BPH: Considerations for Daily Life
Taking certain precautions in daily life is important while living with BPH. Regulating bathroom habits to manage the frequent need to urinate, improving nighttime sleep, and increasing physical activities can be beneficial. Additionally, monitoring symptoms and attending regular doctor checkups can enhance quality of life.
Psychological Effects and Support Methods for BPH
BPH can also create psychological effects. Difficulties with urination and constant discomfort can lead to emotional issues such as stress, anxiety, and depression. Support groups, psychotherapy, and stress management techniques can help alleviate this emotional burden.
Recent Research on BPH and Future Perspectives
Recent research on BPH aims to improve treatment methods and management strategies. New drugs, minimally invasive procedures, and genetic studies are enhancing the understanding of BPH and the development of more effective treatment methods. In the coming years, advancements in this field may provide easier and more effective ways to live with BPH.
Conclusion: Strategies for Managing BPH and Leading a Healthy Life
BPH is a treatable condition that occurs with aging. The management of symptoms can be effectively controlled through lifestyle changes, medication treatment, and other treatment methods. Leading a healthy life and attending regular doctor checkups play an important role in reducing the effects of BPH. These strategies help increase the quality of life, promoting a healthy and comfortable lifestyle.
DO YOU NEED HELP?
Request a Callback Today!
We will usually contact you within 24 hours of your request.
